Laminar micro wind tunnel
To study the aerodynamic aspect of different shapes or scale models of 5 to 6 centimeters long
- Choose a closed room
- The object to study
- A cigarette
- A cigarette lighter
- A ash-tray
- A piece of copper wire
- A pin
- A mass
- An halogen light source
- A black paper
- A camera
Light the cigarette and live it on the ash-tray. Place the model in the smock
Laminar micro wind tunnel
Use incense for non smoker
Aerodynamic drag force formula
Fa = 1/2 r S Cd v2
Fa is aerodynamic drag in newton N
r is air density in kg/m3
S is frontal section of the volume in m2
Cd is the shape coefficient without dimension (Cd cyclist = 0.9 - Cd airplane = 0.027)
v is speed in m/s
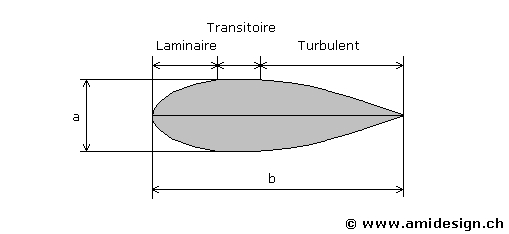
The ideal shape
It is seen immediately that the Cd is important when designing vehicle
The shape to the Cd of 0.04 is represented on figure below
Profile of the best aerodynamic revolution volume
Where "a" represents the width and "b" the length
For a Cd of 0.04 it is necessary to comply with this two rules :
- 1. the maximum width is were the third of the length b
- 2. For a maximum volume, the optimum b/a ratio is 5
The form is traversed by three types of air flow :
- 1. At the front one, a laminar flow where the airflows are parallel to surface and resistance is low and proportional to the speed
- 2. In the center, a transitory flow, the dashes tend to deviate from surface
- 3. A the back, a turbulent flow, the nets tend to follow loops trajectories and resistance is proportional to the square of the speed
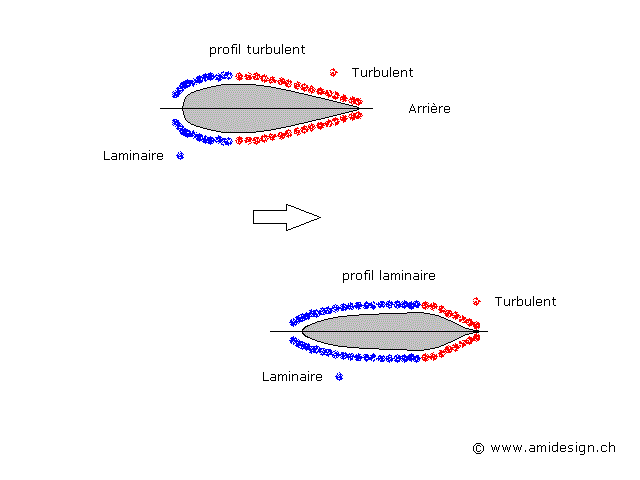
They exist shapes known as laminar which have laminar fields longer and which are better to receive a human body lengthened with the shoulders on the level of the fields transient
These shapes are used for the fuselages of competition sailplane or the body of recumbent bicycle
An example is the Acabion
These shapes are optimal to receive a human body and to offer the minimum of resistance
Half profiles turbulent and laminar
Moreover aerodynamic shapes require a regularity and an irreproachable surface quality
Ideas and suggestions
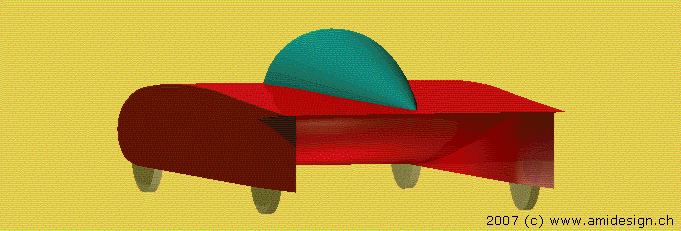
Car with a self-stabilizing profile
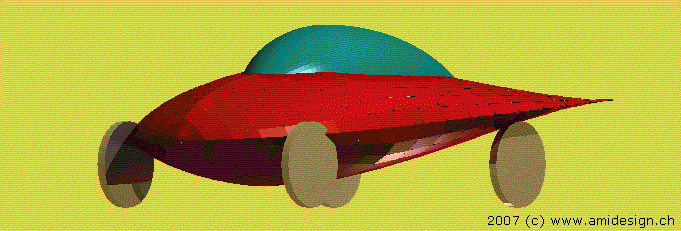
Car with biconvex profile
Oldsmobile Aerotech 1987
413 km/h on circuit, turbo engine 2 liters
Back center of masses
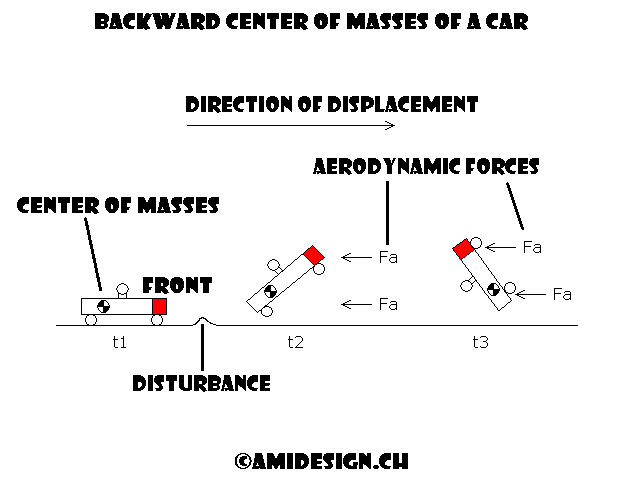
Position of the center of masses of a vehicle
The position of the centre of masses is imposed
It is located between the front quarter and third of the body
The important masses are thus forwards: thermal engine or electric batteries
If the centre of gravity is too back
In case of takeoff the rear passes in front
The vehicle finishes on the roof as shown in the figure below
This rule is important for all vehicle especially for race boats
MG EX 181 "Teardrop"
Record breaker on the Bonneville Salt Flats 1959.